Introduction to Reflective Objectives

Microscope objectives are one of the most recognizable components of a microscope design. Microscope objectives magnify images so they can be viewed easily by the human eye via an eyepiece or by an imaging system (e.g. imaging lens and camera). Traditional objectives are refractive in design; in other words, they are comprised of a series of optical lenses. However, the need for high magnification focusing optics, chromatically corrected from the deep-ultraviolet to the far-infrared, has prompted industry to develop economical off-the-shelf microscope objectives for these wavelengths - reflective, or mirror-based, objectives are the answer. These objectives employ a reflective design of two or more mirrors to focus light or form an image. For more information on objectives in general, view Understanding Microscopes and Objectives.
The most common type of reflective objective is a two-mirror Schwarzschild objective (Figure 1). This system consists of a small diameter "primary" mirror, held in position by a spider mount and a large diameter "secondary" mirror with a center aperture. The primary and secondary mirrors are represented with gold coatings to better illustrate their location within the reflective objective housing. These mirror-based objectives are available in two configurations: infinity corrected for focusing applications and finite conjugate for imaging applications.
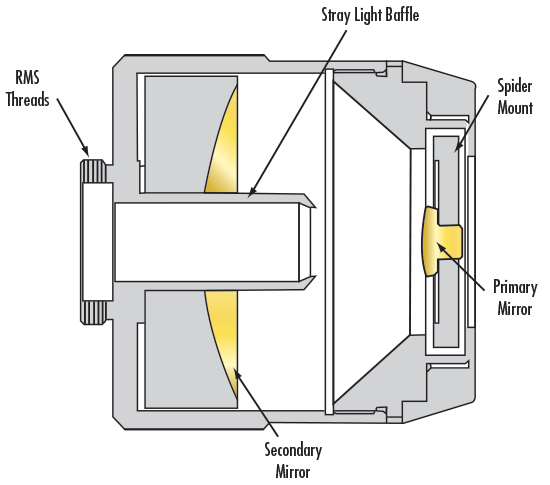
Figure 1: Anatomy of a Reflective Objective
TYPES OF REFLECTIVE OBJECTIVES
Infinity Corrected Reflective Objectives
Infinity corrected reflective objectives (Figure 2) are ideal for focusing applications. Collimated light (e.g. a laser source) enters the objective through the center aperture in the secondary mirror and comes to focus at its specified working distance. This configuration provides an economical means of focusing broadband or multiple laser sources to a single point. A common application is focusing an infrared (IR) or ultraviolet (UV) laser (such as an Nd:YAG laser) which incorporates a visible reference beam.
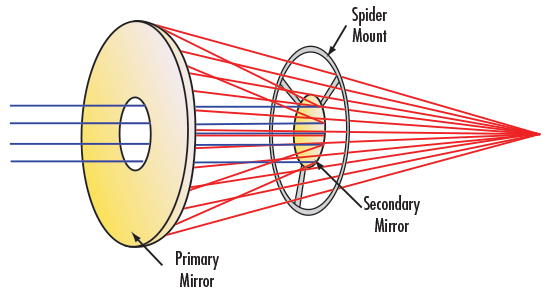
Figure 2: Infinity Corrected Reflective Objective Design
Finite-Conjugate Reflective Objectives
Finite conjugate reflective objectives (Figure 3) are ideal for imaging applications. They are a straightforward solution that does not require the use of any additional focusing optics. This finite conjugate mirror-based configuration provides excellent resolution, and can typically be used interchangeably with traditional refractive microscope objectives. Infinity corrected reflective objectives can be used in imaging applications with the addition of a tube lens and have the added flexibility of introducing beam manipulation optics into the beam path.
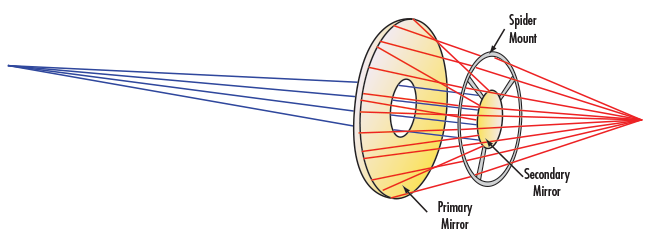
Figure 3: Finite-Conjugate Reflective Objective Design
THE BENEFITS OF REFLECTIVE VS. REFRACTIVE MICROSCOPE OBJECTIVE DESIGNS

The primary advantage of reflective objectives versus their refractive counterparts is their chromatic correction over broad spectral ranges. Refractive objectives that offer similar performance in limited ranges, for example the visible spectrum, are fairly popular. However, as the wavelength range begins to exceed the design range, transmission and image performance suffer. In addition, there are numerous reflective coating options available that allow unmatched performance in the deep-UV, IR, and at specific laser wavelengths.
Important Reflective Objective Specifications
When comparing reflective objectives, there are two parameters unique to these mirror-based systems that need to be considered: obscuration and transmitted wavefront. In reflective systems, there is a central portion of the primary mirror that does not transfer the rays to the secondary mirror but rather reflects them back out through the stray light baffle. To avoid this, many manufacturers place an absorptive coating over the central part of the primary mirror. There are two other locations were obscuration occurs, namely, the diameter of the primary mirror and the width of the spider legs. It is best to include all contribution of obscuration in the stated value, though some manufacturers only include the contribution of the central obscuration. For example, Edmund Optics® includes all contribution of obscuration in specifications for reflective objectives.
Transmitted wavefront error is perhaps the most important parameter for many applications requiring a reflective objective; transmitted wavefront error is the difference between the wavefront from when it enters and exits the system. Recent advances in mirror manufacturing enable production and testing of high accuracy surfaces, creating better corrected systems. Mirrors on the order of λ/20 peak-to-valley (P-V) are achievable and these allow the production of reflective objectives that have a transmitted wavefront ≤ λ/4 P-V. For example, Edmund Optics hard-mounts all fixed TECHSPEC® ReflX™ Reflective Objectives, guaranteeing λ/10 RMS transmitted wavefront on the standard line and λ/4 P-V transmitted wavefront on the high performance line. The fixed line of TECHSPEC® ReflX™ Reflective Objectives is actively aligned and tested on a Zygo GPI-XP Interferometer to ensure that each objective is within specification.
While traditional refractive objectives are ideal for a range of applications within a specific wavelength band, reflective objectives can be substituted to increase performance and image quality in broadband applications from the deep-UV to the far-IR. Reflective objectives are ideal for FTIR, laser focusing, and ellipsometry applications where diffraction-limited performance and chromatic correction are crucial.
版權(quán)所有 © 2025 江陰韻翔光電技術(shù)有限公司 備案號(hào):蘇ICP備16003332號(hào)-1 技術(shù)支持:化工儀器網(wǎng) 管理登陸 GoogleSitemap